|
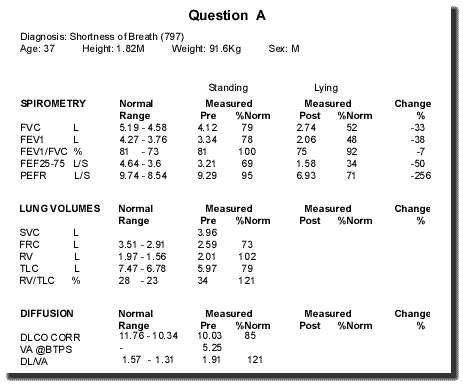
1. What is the significance of the spirometry results ?
2. What size of change is usually regarded as abnormal ?
3. What confirmatory tests could be performed ?
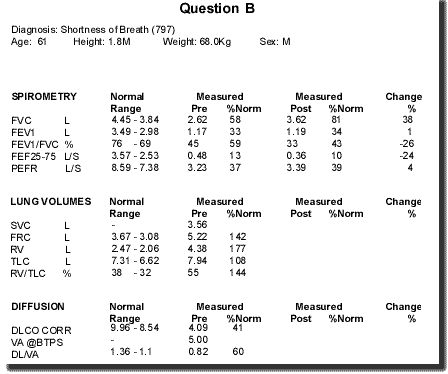
4. What is the prognosis in most cases ? 1. What is this form of abnormal f/v curve due to ?
2. What condition does it characterise ?
3. Interpret the lung volumes.
4. Why is the VA so much lower than the TLC ?
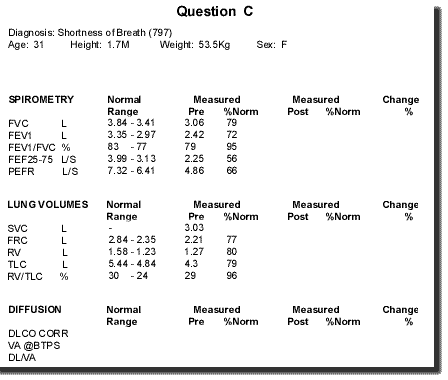
1. What pattern of abnormality is seen here ?
2. What is the possible cause of this pattern of abnormality ?
3. The F/V expiratory curve has a serrated appearance. Of which condition is this said to be characteristic ?
4. Why is it characteristic ?
Question A 1. What is the significance of the spirometry results? fall in FEV1 suggests diaphragmatic paresis. 2. What size of change is usually regarded as abnormal? 15% fall in FEV1 3. What confirmatory tests could be performed to establish the diagnosis? US of diaphragm and / or phrenic nerve stimulation 4. What is the prognosis in most cases? generally good with significant return of function in idiopathic or post viral cases over a 3 year period
Question B 1. what is this form of abnormal f/v curve due to? pressure dependent airway collapse 2. what condition does it characterise? emphysema 3. interpret the lung volumes. gas trapping 4 why is the VA so much lower than the TLC? gas trapping leading to poor gas mixing on the single breath test
QUESTION C 1. what pattern of abnormality is seen here? restrictive 2. what are the possible causes of this pattern of abnormality? weak muscles / ILD / msk deformity 3. the f/v expiratory curve has a serrated appearance. Of which condition is this said to be characteristic? SAS 4. Why? Variable collapsibility producing oscillation of airway calibre during expiration.
|