High Resolution Tomography (HRCT)
Of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
Dr Indera Mootosamy
It is now well accepted that High Resolution Computerized Tomography (HRCT) is superior to the plain Chest Xray in the assessment of Chronic Diffuse Infiltrative Lung Disease. The Chest Xray may show no abnormality whilst the HRCT may demonstrate extensive parenchymal lung disease(1).
HRCT is the established imaging modality to assess Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF).It is characterised by reticular opacities found mainly in the subpleural and lung base areas (2) (Fig 1).These correspond to sites of irregular fibrosis reflecting the pathological finding of (UIP-Usual Interstitial Pneumonia) (3).Irregular pleural, bronchial and vascular interfaces are caused by these (fig 1)and can be coarse or fine (2). Thickening of the interlobular septae in an irregular manner (Fig 1.) and ot the intralobular lines is also found (4).
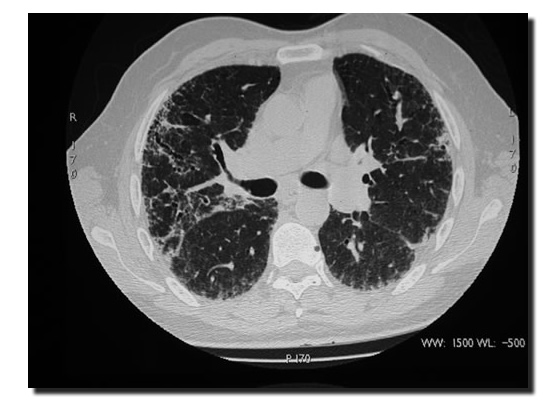
Fig 1. Reticular opacities seen at lung interface with the pleura
Severe fibrosis leads to traction bronchiectasis (3) (FIG 2).
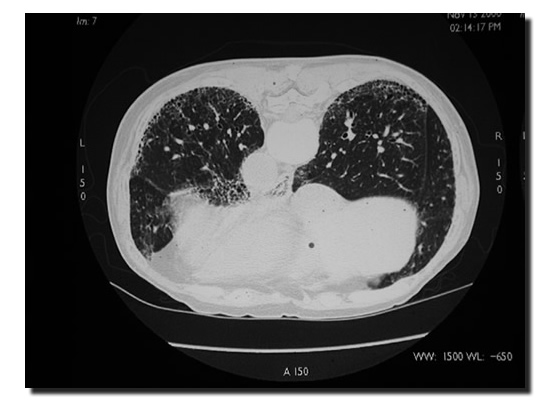
Fig 2. Traction bronchiectasis in both lower lobes Patchy ground glass shadowing seen bilaterally
Cystic areas (honeycomb shadowing) of 2-20 mm occur often in (IPF), are associated with the reticular opacities and may be seen in 90% of HRCT (2) (Fig 3.). When active disease or alveolitis is seen in IPF ground glass shadowing is commonly seen and is indicative of DIP (Disquamative Interstitial Pneumonia) (3) (Fig 2.) and may respond to steoid therapy. The distribution of IPF on HRCT can be patchy Predominating in the subpleural and peripheral regions (3).
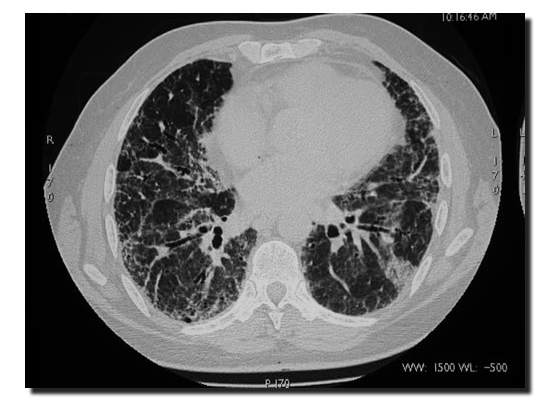
Fig 3. Prone HRCT showing fine honey comb shadowing at the lung bases
References.:-
(1)N L Muller computer Tomography in Chronic Interstitial Lung Disease. Imaging of Diffuse Lung diseases, Radiological Clinics Of North America- Vol.29.no5, September1991 1085-1093
(2) NLMuller, RR Miller Computerised tomography of Chronic Diffuse Infiltrative Lung Disease Part 1 Am Rev. Respir Dis 1990; 142: 1206-1215
(3) WRWebb NLMuller D Naidich Chapter 5 High Resolution CT of the Lung 1st ed 1992 Raven Press
(4) G Gamsu JS Klein High Resolution Computre Tomography of diffuse Lung Disease Clinical Radiology 1989 ,40, 554-556