

|
|
Grammar Terms |
Noun | - Noun Plurals |
| Pronoun Article Case Preposition Adjective Adverb |
|||
These simple explanations are intended |
Sentence, Clause, Phrase, Conjunction |
||
| - Infinitive and Participles - Tense - Simple and Continuous forms - Voice - Mood - Conditionals - Modals | |||

Noun
A Noun is a word which names:
a living creature: person, ____, ____, ____, ____ an inanimate object: vehicle, ____, ____, ____, ____ a place: town, ____, ____ an event, activity or process: exhibition, ____, ____ an idea or concept: inspiration, ____, ____
Complete the table, allocating the following words to an appropriate category:
animal - home - country - action - development - bird - machine
tree - faith - house - garden - insect - creativity - reptile
Check the Solution afterwards.
Solution: Noun
a living creature: person, animal, bird, insect, reptile an inanimate Object: vehicle, machine, tree, house, garden a place: town, home, country an event, activity or process: exhibition, action, development an idea or concept: inspiration, creativity, faith
Noun Plurals
Most English Nouns form their plural by adding s. Irregular Nouns are for example, child/children, mouse/mice, woman/women.
Some Nouns, like creativity, flour and weather do not have a Plural.
Tip: Other languages act differently - it's a good idea to learn the Plural of each new Noun as you meet it.
Pronoun
A Pronoun is used instead of a Noun.There are different kinds of Pronouns: Personal, Interrogative, Demonstrative, Impersonal.
Can you complete the table, highlighting the Pronouns and allocating the appropriate category?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Personal Pronoun He thought she would come with us ? Pronoun Nobody knows what the answer might be ? Pronoun In your opinion, who or what is causing the problem? ? Pronoun The team think this is the best solution
Solution: Pronoun
Personal Pronoun He thought she would come with us Impersonal Pronoun Nobody knows what the answer might be Interrogative Pronoun In your opinion, who or what is causing the problem? Demonstrative Pronoun The team think this is the best solution
Article
In English, the Definite Article = the, and is used to designate a particular item, eg: the day we met.
The Indefinite article = a (or an before a vowel) is used to designate an indefinite item, eg: a summer's day, an early start.
Note: The use of articles can differ from language to language!
Case
'Case' concerns the function of certain words or groups of words within a sentence. There are four Cases in English and German: Subject, Object, Indirect Object, Possessive. The dictionary uses Latin terms: Nominative, Accusative, Dative, Genitive, so you'll need to recognise these. Don't be put off by terminology, though - you successfully use Case in your everyday use of English!
The following verse (source unkown) illustrates all four Cases. Consider the notes below and see how the different words and phrases behave in each Case (!)
Subject Case (Nominative)
I in line 1 and the moon in line 2 are 'in charge of the action' of the Verb. They are said to be in the Subject Case (Nominative Case in Latin terminology).The Subject governs the Verb.
The Subject of the Verb can be a Noun, a Phrase, a Pronoun or a Clause.Check out the examples below, with Subjects:
- governing Verbs in the Active Voice, where the Subject is in charge of the action
- governing Verbs in the Passive Voice, where the Subject experiences the action
Can you complete the table, highlighting the Subject in each line, and supplying the correct category?
Check the Solution afterwards.
? Fruit is a healthy part of a diet
Fruit is eaten as part of a healthy dietPronoun This seems to be the best solution
This was identified as the best solution? Lack of communication is causing the problem
Lack of communication was seen to cause the problem? What happens next will come as a big surprise
What happens next will be widely reported
Solution: Subject Case (Nominative)
Noun Fruit is a healthy part of a diet
Fruit is eaten as part of a healthy dietPronoun This seems to be the best solution
This was identified as the best solutionPhrase Lack of communication is causing the problem
Lack of communication was seen to cause the problemClause What happens next will come as a big surprise
What happens next will be widely reported
Object Case (Accusative)
the moon in line 1 and me in line 2 are functioning as the Object of the Verb (Accusative Case in Latin terminology). The same moon - and the same person - are represented from a different perspective in each line. In line 2 for example, the moon is governing the action of the Verb (as Subject of the Verb) and me is the Object of the Verb's attention.
The Object of the Verb can be a Noun, a Clause, a Pronoun or a Phrase. Look at the examples below.
Can you complete the table?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Noun He likes fruit ? Don't eat it! ? We must address the lack of communication ? You'll see that he was right
Solution: Object Case (Accusative)
Noun He likes fruit Pronoun Don't eat it! Phrase We must address the lack of communication Clause You'll see that he was right
Indirect Object Case (Dative) and Possessive Case (Genitive)

The Indirect Object of the Verb is whatever or whoever receives the action of the Verb indirectly. Here the phrase the leaves fulfils the Indirect Object function - hence it is in the Indirect Object Case (Dative Case in Latin terminology).
The following phrase is an example of the Possessive Case (the Latin term is the Genitive), which as the name implies, denotes ownership:
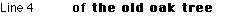
Look at the examples below: Can you complete the table?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Indirect Object Case Our company delivers spare parts to a network of dealers Possessive Case Greta's hair is beautiful! ? Case I've forgotten the title of the book ? Case He did them no favours. ? Case Here's another enquiry from that company ? Case What can I wear with this suit? ? Case The neighbour's cat has gone missing again
Solution: Indirect Object Case (Dative), Possessive Case (Genitive)
Indirect Object Case Our company delivers spare parts to a network of dealers Possessive Case Greta's hair is beautiful! Possessive Case I've forgotten the title of the book Indirect Object Case He did them no favours. Indirect Object Case Here's another enquiry from that company Indirect Object Case What can I wear with this suit? Possessive Case The neighbour's cat has gone missing again
Preposition
Essentially a Preposition is a word which gives information on the position of something (eg: person, object, action) in space or time.
Examples of Prepositions:
in - on - over - up - out - through - after - before
Adjective
Adjectives describe someone or something. As well as the basic form, there are Comparative and Superlative forms:
Basic kind, nice, exciting Comparative kinder, nicer, more exciting Superlative kindest, nicest, most exciting
Can you identify the adjective and its category to complete the table below?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Basic That's interesting, if you think about it ? I think we got the best deal, don't you? ? Buy it - it's faster and it's less expensive! ? Yes, but it doesn't give the smoothest ride! ? This doesn't get any easier ? A typical sort of reply, if you ask me
Solution: Adjective
Basic That's interesting, if you think about it Superlative I think we got the best deal, don't you? Comparative Buy it - it's faster and it's less expensive! Superlative Yes, but it doesn't give the smoothest ride! Comparative This doesn't get any easier Basic A typical sort of reply, if you ask me
Adverb
Adverbs determine how something is done. They can determine Verbs, Adjectives or other Adverbs.
Can you complete the table below, identifying the Adverb and its function in each line?
Check the Solution afterwards.
determining a Verb She drives carefully determining an Adjective She is extremely careful determining another Adverb She drives really carefully determining ? It fits very well determining ? That's quite good determining ? That works well
Solution: Adverb
determining a Verb She drives carefully determining an Adjective She is extremely careful determining another Adverb She drives really carefully determining another Adverb It fits very well determining an Adjective That's quite good determining a Verb That works well
Sentence, Clause, Phrase
Sentence A Sentence is a combination of words which makes sense. There's at least one Verb in every sentence, eg:
A Sentence is a combination of words which makes sense. There's at least one Verb in every Sentence Clause A sentence can be made up of one Clause or several Clauses, usually linked by conjunctions:
A Sentence is a combination of words which makes sense (and it can be) (,) made up of one Clause or several Clauses. Main Clause A Main Clause makes sense on its own:
He is always on time I told them everything It was already quite late Subordinate Clause A Subordinate Clause contains at least one Verb, but is subordinate to the idea in the Main Clause. It does not make sense on its own. Some examples:
... because he lives nearby When I realised that, .... ....so he couldn't come Relative Clause This contains at least one Verb, but it relates to a word or idea in the Main Clause and does not make sense on its own.Some examples:
(...the car) which you like (...the man) who came (...the dress) she wore Phrase A Phrase is a meaningful group of words, which may or may not contain a Verb, eg:
in a hurry before too long living dangerously
Can you complete the table below, identifying Verbs, complete Sentences, Clauses and Phrases?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Sentence I've lost my pen again ? Because she had forgotten what to do ? I'm going to the party tonight ? There's a message for you on the answerphone ? The boys started school yesterday, as a matter of fact ? Although they knew all about it ? Tea, coffee, milk, bread, sugar - what else do I need? ? He took one look at the note and left the room ? the luck of the draw ? in the rain
Solution: Sentence, Clause, Phrase
Sentence I've lost my pen again Subordinate Clause Because she had forgotten what to do Sentence I'm going to the party tonight Sentence There's a message for you on the answerphone Sentence The boys started school yesterday, as a matter of fact Subordinate Clause Although they knew all about it Sentence Tea, coffee, milk, bread, sugar - there's something else, though, I think Sentence He took one look at the note and left the room Phrase the luck of the draw Phrase in the rain
Conjunction
As the term suggests, a conjunction joins words, phrases or clauses together. Co-ordinating conjunctions join items of 'equal' value. Subordinating conjunctions introduce a Subordinate Clause (a clause which does not make sense on its own).
Consider the sentences below. Can you identify the conjunctions and their type?
Check the Solution afterwards.
We use ready-made parts from Hamburg and assemble the product here Co-ordinating 
If you want a quarrel, you're going the right way about it!
? I don't often eat out, but I do enjoy it! ? We can do it while you wait ? Exchange the goods straight away, or my boss will cancel the entire order! ? While I was waiting for you, I heard an announcement ? The plants survived despite the frost ? No I can't stay, because I've got to be at work early tomorrow! ? I'm usually out and about with friends, although I sometimes stay at home too ?
Solution: Conjunctions
We use ready-made parts from Hamburg and assemble the product here Co-ordinating If you want a quarrel, you're going the right way about it! Subordinating I don't often eat out, but I do enjoy it! Co-ordinating We can do it while you wait Subordinating Exchange the goods straight away, or my boss will cancel the entire order! Co-ordinating While I was waiting for you, I heard an announcement Subordinating The plants survived despite the frost Subordinating No I can't stay, because I've got to be at work early tomorrow! Subordinating I'm usually out and about with friends, although I sometimes stay at home too Subordinating
Verb
What are Verbs? In a nutshell, Verbs are being words (like 'become') or doing words (like 'worked'):
- Being words express a state, eg: It's becoming easier.
- Doing words express an action, eg: They work hard at German.
There is a Verb in every sentence.
Can you allocate the Verbs in the list to the right category, to complete the table below?
Check the Solution afterwards.
will exist - does - was - became - doing - had been - did - done
shall do - consisted - to subsist - thinks - thinking - being - has seen
Doing words express action: to do, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____ Being words express a state: to be, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____
Solution: What are Verbs?
Doing words express action: to do, does, doing, did, done, shall do, thinks, thinking, has seen Being words express a state: to be, is, being, had been, consisted, will exist, to subsist, became, was
Infinitive and Participle
Infinitive
In the dictionary the main entry of the Verb is in the Infinitive.
Participle
Each Verb has two Participles:
- Present Participle
- Past Participle
As the name suggests, these are parts of the Verb. They can be used in combination with an Auxiliary Verb like to be and to have to express Tense or Form.
Can you identify the infinitives and participles, then allocate them to the right category to complete the table below?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Infinitive I have a lot to do this morning Past Participle What have you done? ? We're all working hard ? They are definitely coming to the party ? We had left by the time they arrived ? She didn't know what to say to him ? Are you planning a surprise for his birthday? ? That's a lot to pay for such a service ? He's bought another new jacket
Solution: Infinitive and Participle
Infinitive I have a lot to do this morning Past Participle What have you done? Present Participle We're all working hard Present Participle They are definitely coming to the party Past Participle We had left by the time they arrived Infinitive She didn't know what to say to him Present Participle Are you planning a surprise for his birthday? Infinitive That's a lot to pay for such a service Past Participle He's bought another new jacket
Tense
The tense of the Verb has to do with the time to which the Verb relates, for example: a Past, Present or Future action or state.
These are the six basic tenses:
Present
Present Perfect
Past
Past Perfect
Future
Future Perfect
Can you complete the table by identifying the Verb construction and tense?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Present He enjoys his work ? I'll have done it by next week ? He's passed his driving test ? They enjoyed the play ? They had not been there before ? They are over there ? He'll be there on time ? He had heard enough ? She's been home all day ? She was home all day ? I have enjoyed your company ? It will have been done by then
Solution: Tense
Present He enjoys his work Future Perfect I'll have done it by next week Present Perfect He's passed his driving test Past They enjoyed the play Past Perfect They had not been there before Present They are over there Future He'll be there on time Past Perfect He had heard enough Future I'll be home all day Past She was home all day Present Perfect I have enjoyed your company Future Perfect It will have been done by then
Voice
Active Voice
When the Subject is in charge of the Action, we say that the Verb is in the Active Voice.
Your dog (Subject) bit (Action) me!
Passive Voice
A Verb is in the Passive Voice when the Subject receives the Action:
I (Subject) have been bitten by your dog!
Consider the examples below. Identify the Verbs and allocate Active or Passive Voice as appropriate.
Check the Solution afterwards.
Active The news surprised us a bit! ? The car will have to be sold soon ? They 're going to France next week ? We were quite shocked by that ? A different tale was told to me ? The waves lashed the shore
Solution: Voice
Active The news surprised us a bit! Passive The car will have to be sold soon Active They 're going to France next week Passive We were quite shocked by that Passive A different tale was told to me Active The waves lashed the shore
Mood
English Verbs can be in three moods or modes: Indicative, Imperative, Subjunctive.
Indicative
The Indicative mood indicates a real or likely action or state and is the most common mood or mode:
My parents live in Elswick Gordon and Jill are on holiday again Imperative
The Imperative expresses an order or command. There is only one tense:
Come here! Be careful! Subjunctive
The Subjunctive mood indicates the initiator's attitude towards the action or state, for example it expresses hopes, uncertainties:
I wish he were here now I advise she be more careful
Can you identify the Verb structures and moods to complete the table?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Imperative Go away! ? I'll take half a dozen of those ? Were we only rich! ? Think about it ? Glory be to God in the Highest ? That's it, then!
Solution: Mood
Imperative Go away! Indicative I'll take half a dozen of those Subjunctive Were we only rich! Imperative Think about it Subjunctive Glory be to God in the highest Indicative That's it, then!
Simple and Continuous forms
English Verbs have a Simple Form and a Continuous Form.
Present Simple
This indicates a present action or state. It can be:
right now: I hear what you say I'm not hungry habitual: He goes for a walk every day She 's never late emphatic: She does agree with you It is easier! Present Continuous
This structure: 'to be' + Present Participle (see below) is used when something is:
in the process of happening: He's out walking the dog She 's being very careful right now intended/about to happen: We're buying a new car I'm being early tonight The Continuous Form allows users to be somewhat vague,which can be quite convenient, for example: I'm working on it!
Other tenses
These are formed following the same principles.
Can you identify Verb structures to complete the table?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Continuous form He was walking the dog ? We'll be getting a new car ? They came later ? I was early that night ? He was growing tired ? You've been warned ? When will she be here? ? You are being super careful ? It had come too late ? I'll be there! ? It's getting dark
Solution: Simple and Continuous forms
Continuous form He was walking the dog Continuous form We'll be getting a new car Simple form They came later Simple form I was early that night Continuous form He was growing tired Simple form You've been warned! Simple form When will she be here? Continuous form You are being super careful Simple form It had come too late Simple form I'll be there! Continuous form It's getting dark
Conditionals
There are two Conditional forms of the Verb:
Conditional 1
In English this is formed with would + Infinitive
Conditional 2
In English this is formed with would have + Past Participle
Below are three examples of stating a condition. Only the second two use Conditionals:
Present tense/Future 1 If he comes, I shall leave! Past Subjunctive/Conditional 1 If I were you, I'd leave! Past Perfect tense/Conditional 2 If he had come, I would have left!
Can you identify the Structures and Verbs to complete the table below?
Check the Solution afterwards.
Present tense / Future 1 If he comes, I shall leave! ? If he were here, we'd start the meal ? If you lend me that now I'll give it back later ? If I didn't go he'd be disappointed ? If you'd said nothing they would have agreed ? When she arrives we'll tell her about it ? If you hadn't done that, you wouldn't have lost ? If you did that I'd die laughing ? If they knew him better they'd trust him more ? If you'd been there you'd have loved it!
Solution: Conditionals
Present tense/Future 1 If he comes, I shall leave! Past Subjunctive/Conditional 1 If he were here, we'd start the meal Present tense/Future 1 If you lend me that I'll give it back later Past Subjunctive/Conditional 1 If I didn't go he'd be disappointed Past Perfect tense/Conditional 2 If you'd said nothing they would have left Present tense/Future 1 When she arrives we'll tell her about it Past Perfect tense/Conditional 2 If you hadn't done it, you wouldn't have lost Past Subjunctive/Conditional 1 If you did that I'd die laughing Past Subjunctive/Conditional 1 If they knew him better they'd trust him more Past Perfect tense/Conditional 2 If you'd been there you'd have loved it!
Modals
This is a group of Verbs which indicate the mode or manner of an action or state expressed by another Verb. The other Verb is then referred to as the Main Verb, and is sometimes implied.
Some examples:
I can't (be there before ten) We should (go now) You ought to (be pleased) Must you (do that)? May I (help you)? Couldn't you (do it)? Some English modals (like must) only exist in the one form. Can has one other form: could.
For all other tenses English speakers have to use alternative expressions.
Can you find alternative expressions to complete the table below?
Check the Solution afterwards.
must to have to I'll have to go now can to ? He wasn't ____ save the goal may to ? Nobody will ____ join after that date should to ? You ____ have done it by now
Solution: Modals
must to have to I'll have to go now can to be able to He wasn't able to save the goal may to be allowed to Nobody will be allowed to join after that date should to be to You were to have done it by now